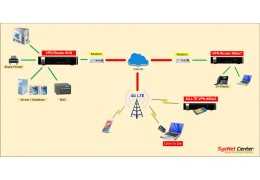
Review ทดสอบใช้งาน Reyee RG-EG406XS Router, Internet Throughput, Loadbalance, เก็บ Log Internet ตาม พรบ, L2TP...


Review ทดสอบใช้งาน Reyee RG-EG406XS Router, Internet Throughput, Loadbalance, เก็บ Log Internet ตาม พรบ, L2TP...





Support / ติดตั้งด้วยทีมงาน Certificate
สอบถามข้อมูลสินค้าเพิ่มเติม
LINE ID: @sysnet โทร: 02 102 4284
Click ต้องการใบเสนอราคา
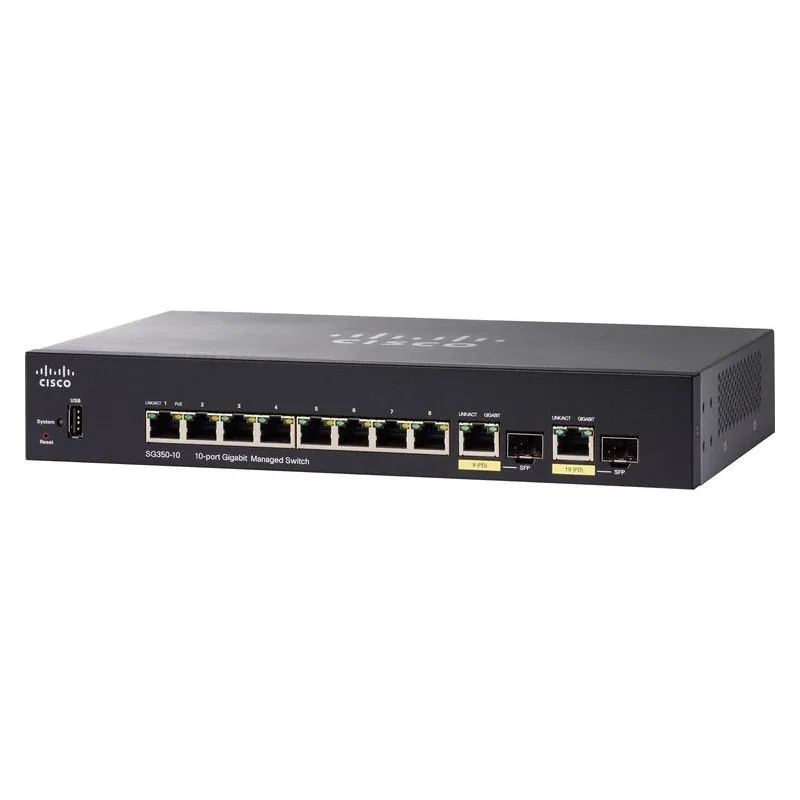
Cisco SG350 Series Switches Data Sheet
Product Specification | |
Overview | Cisco SG350-10 L3-Managed Switch 8 Port Gigabit พร้อม 2 Port Combo รองรับ SFP Module หรือ เลือกเป็น Port Lan ความเร็ว Gigabit 2 Port รองรับ Static Routing, VLANs ควบคุมผ่าน Web |
| เหมาะใช้สำหรับเชื่อมต่อกับระบบเครือข่ายภายในสำนักงานที่ต้องการความเร็วสูงสุดหรือทำเป็น Core Switch |
Combo Ports | 2 Port SFP/ 2 Port RJ45 |
LAN Port | 8Port ความเร็ว 10/100/1000Mbps แบบ RJ-45 (Support Auto-Negotiation and Auto MDI/X) |
| Switching Capacity | Capacity in Millions of Packets per Second (64-byte packets) 14.88 mpps Switching Capacity in Gigabits per Second 20 Gbps |
| USB Slot | For file-management purposes |
| Layer 2 Switching | Spanning Tree Protocol Standard 802.1d Spanning Tree support Fast convergence using 802.1w (Rapid Spanning Tree [RSTP]), enabled by default 8 instances are supported Multiple Spanning Tree instances using 802.1s (MSTP) Port Grouping Support for IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) • Up to 8 groups • Up to 8 ports per group with 16 candidate ports for each (dynamic) 802.3ad link aggregation VLAN Support for up to 4096 VLANs simultaneously Port-based and 802.1Q tag-based VLANs MAC-based VLAN Management VLAN Private VLAN Edge (PVE), also known as protected ports, with multiple uplinks Guest VLAN Unauthenticated VLAN Dynamic VLAN assignment via RADIUS server along with 802.1x client authentication CPE VLAN Voice VLAN Voice traffic is automatically assigned to a voice-specific VLAN and treated with appropriate levels of QoS Auto voice capabilities deliver network-wide zero-touch deployment of voice endpoints and call control devices Multicast TV VLAN Multicast TV VLAN allows the single multicast VLAN to be shared in the network while subscribers remain in separate VLANs (also known as MVR) Q-in-Q VLAN VLANs transparently cross a service provider network while isolating traffic among customers Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)/Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) Protocols for automatically propagating and configuring VLANs in a bridged domain Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) UDLD monitors physical connection to detect unidirectional links caused by incorrect wiring or cable/port faults to prevent forwarding loops and blackholing of traffic in switched networks Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Relay at Layer 2 Relay of DHCP traffic to DHCP server in different VLAN; works with DHCP Option 82 Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) versions 1, 2, and 3 snooping IGMP limits bandwidth-intensive multicast traffic to only the requesters; supports 1K multicast groups (source-specific multicasting is also supported) IGMP Querier IGMP querier is used to support a Layer 2 multicast domain of snooping switches in the absence of a multicast router Head-of-line (HOL) blocking HOL blocking prevention Jumbo frames Up to 9K (9216) bytes |
| Layer 3 Routing | IPv4 routing Wirespeed routing of IPv4 packets Up to 512 static routes and up to 128 IP interfaces Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR) Support for CIDR Layer 3 Interface Configuration of Layer 3 interface on physical port, LAG, VLAN interface, or loopback interface DHCP relay at Layer 3 Relay of DHCP traffic across IP domains User Datagram Protocol (UDP) relay Relay of broadcast information across Layer 3 domains for application discovery or relaying of bootP/DHCP packets DHCP Server Switch functions as an IPv4 DHCP server serving IP addresses for multiple DHCP pools/scopes Support for DHCP options |
| Security | Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol SSH is a secure replacement for Telnet traffic. SCP also uses SSH. SSH v1 and v2 are supported Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL support: Encrypts all HTTPS traffic, allowing highly secure access to the browser-based management GUI in the switch IEEE 802.1X (Authenticator role) 802.1X: RADIUS authentication and accounting, MD5 hash; guest VLAN; unauthenticated VLAN, single/multiple host mode and single/multiple sessions Supports time-based 802.1X Dynamic VLAN assignment Web-based authentication Web based authentication provides network admission control through web browser to any host devices and operating systems STP Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) Guard A security mechanism to protect the network from invalid configurations. A port enabled for BPDU Guard is shut down if a BPDU message is received on that port STP Root Guard This prevents edge devices not in the network administrator's control from becoming Spanning Tree Protocol root nodes DHCP snooping Filters out DHCP messages with unregistered IP addresses and/or from unexpected or untrusted interfaces. This prevents rogue devices from behaving as DHCP Servers IP Source Guard (IPSG) When IP Source Guard is enabled at a port, the switch filters out IP packets received from the port if the source IP addresses of the packets have not been statically configured or dynamically learned from DHCP snooping. This prevents IP Address Spoofing Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) The switch discards ARP packets from a port if there are no static or dynamic IP/MAC bindings or if there is a discrepancy between the source or destination addresses in the ARP packet. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks IP/MAC/Port Binding (IPMB) The preceding features (DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard, and Dynamic ARP Inspection) work together to prevent DOS attacks in the network, thereby increasing network availability Secure Core Technology (SCT) Makes sure that the switch will receive and process management and protocol traffic no matter how much traffic is received Secure Sensitive Data (SSD) A mechanism to manage sensitive data (such as passwords, keys, and so on) securely on the switch, populating this data to other devices, and secure autoconfig. Access to view the sensitive data as plaintext or encrypted is provided according to the user-configured access level and the access method of the user Layer 2 isolation Private VLAN Edge (PVE) with community VLAN PVE (also known as protected ports) provides Layer 2 isolation between devices in the same VLAN, supports multiple uplinks Port security The ability to lock source MAC addresses to ports and limits the number of learned MAC addresses RADIUS/TACACS+ Supports RADIUS and TACACS authentication. Switch functions as a client Storm control Broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast RADIUS accounting The RADIUS accounting functions allow data to be sent at the start and end of services, indicating the amount of resources (such as time, packets, bytes, and so on) used during the session DoS prevention Denial-of-service (DOS) attack prevention ACLs Support for up to 512 rules Drop or rate limit based on source and destination MAC, VLAN ID or IP address, protocol, port, differentiated services code point (DSCP)/IP precedence, TCP/UDP source and destination ports, 802.1p priority, Ethernet type, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets, IGMP packets, TCP flag, time-based ACLs supported. |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | Priority levels 8 hardware queues Scheduling Strict priority and weighted round-robin (WRR) Queue assignment based on DSCP and class of service (802.1p/CoS) Class of service Port based; 802.1p VLAN priority based; IPv4/v6 IP precedence/type of service (ToS)/DSCP based; differentiated services (DiffServ); classification and remarking ACLs, trusted QoS Rate limiting Ingress policer; egress shaping and rate control; per VLAN, per port, and flow based Congestion avoidance A TCP congestion avoidance algorithm is required to minimize and prevent global TCP loss synchronization. |
| Standards | IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet, IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet, IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3ad LACP, IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3x Flow Control, IEEE 802.1D (STP, GARP, and GVRP), IEEE 802.1Q/p VLAN, IEEE 802.1w RSTP, IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP, IEEE 802.1X Port Access Authentication, IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at, RFC 768, RFC 783, RFC 791, RFC 792, RFC 793, RFC 813, RFC 879, RFC 896, RFC 826, RFC 854, RFC 855, RFC 856, RFC 858, RFC 894, RFC 919, RFC 922, RFC 920, RFC 950, RFC 1042, RFC 1071, RFC 1123, RFC 1141, RFC 1155, RFC 1157, RFC 1350, RFC 1533, RFC 1541, RFC 1624, RFC 1700, RFC 1867, RFC 2030, RFC 2616, RFC 2131, RFC 2132, RFC 3164, RFC 3411, RFC 3412, RFC 3413, RFC 3414, RFC 3415, RFC 2576, RFC 4330, RFC 1213, RFC 1215, RFC 1286, RFC 1442, RFC 1451, RFC 1493, RFC 1573, RFC 1643, RFC 1757, RFC 1907, RFC 2011, RFC 2012, RFC 2013, RFC 2233, RFC 2618, RFC 2665, RFC 2666, RFC 2674, RFC 2737, RFC 2819, RFC 2863, RFC 1157, RFC 1493, RFC 1215, RFC 3416 |
| IPv6 | IPv6 IPv6 host mode IPv6 over Ethernet Dual IPv6/IPv4 stack IPv6 neighbor and router discovery (ND) IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration Path maximum transmission unit (MTU) discovery Duplicate address detection (DAD) ICMP version 6 IPv6 over IPv4 network with Intrasite Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) support USGv6 and IPv6 Gold Logo certified IPv6 QoS Prioritize IPv6 packets in hardware IPv6 ACL Drop or rate limit IPv6 packets in hardware IPv6 First Hop Security RA guard ND inspection DHCPv6 guard Neighbor binding table (snooping and static entries) Neighbor binding integrity check Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD v1/2) snooping Deliver IPv6 multicast packets only to the required receivers IPv6 applications Web/SSL, Telnet server/SSH, ping, traceroute, Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), SNMP, RADIUS, syslog, DNS client, Telnet Client, DHCP Client, DHCP Autoconfig, IPv6 DHCP Relay, TACACS IPv6 RFCs supported RFC 4443 (which obsoletes RFC2463): ICMP version 6 RFC 4291 (which obsoletes RFC 3513): IPv6 address architecture RFC 4291: IPv6 addressing architecture RFC 2460: IPv6 specification RFC 4861 (which obsoletes RFC 2461): neighbor discovery for IPv6 RFC 4862 (which obsoletes RFC 2462): IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration RFC 1981: path MTU discovery RFC 4007: IPv6 scoped address architecture RFC 3484: default address selection mechanism RFC 5214 (which obsoletes RFC 4214): ISATAP tunneling RFC 4293: MIB IPv6: textual conventions and general group RFC 3595: textual conventions for IPv6 flow label |
| Management | Web user interface Built-in switch configuration utility for easy browser-based device configuration (HTTP/HTTPS). Supports configuration, system dashboard, system maintenance, and monitoring SNMP SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3 with support for traps, and SNMP version 3 user-based security model (USM) Remote Monitoring (RMON) Embedded RMON software agent supports 4 RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms, and events) for enhanced traffic management, monitoring, and analysis IPv4 and IPv6 dual stack Coexistence of both protocol stacks to ease migration Firmware upgrade ? Web browser upgrade (HTTP/HTTPS) and TFTP and upgrade over SCP running over SSH ? Upgrade can be initiated through console port as well ? Dual images for resilient firmware upgrades Port mirroring Traffic on a port can be mirrored to another port for analysis with a network analyzer or RMON probe. Up to 8 source ports can be mirrored to one destination port. A single session is supported VLAN mirroring Traffic from a VLAN can be mirrored to a port for analysis with a network analyzer or RMON probe. Up to 8 source VLANs can be mirrored to one destination port. A single session is supported DHCP (options 12, 66, 67, 82, 129, and 150) DHCP options facilitate tighter control from a central point (DHCP server) to obtain IP address, autoconfiguration (with configuration file download), DHCP relay, and hostname Secure Copy (SCP) Securely transfer files to and from the switch Autoconfiguration with Secure Copy (SCP) file download Enables secure mass deployment with protection of sensitive data Text-editable config files Config files can be edited with a text editor and downloaded to another switch, facilitating easier mass deployment Smartports Simplified configuration of QoS and security capabilities Auto Smartports Applies the intelligence delivered through the Smartport roles and applies it automatically to the port based on the devices discovered over Cisco Discovery Protocol or LLDP-MED. This facilitates zero-touch deployments Textview CLI Scriptable command-line interface. A full CLI as well as a menu-based CLI is supported. User privilege levels 1, 7, and 15 are supported for the CLI Cloud services Support for Cisco Small Business FindIT Network Localization Localization of GUI and documentation into multiple languages Other management Traceroute; single IP management; HTTP/HTTPS; SSH; RADIUS; port mirroring; TFTP upgrade; DHCP client; BOOTP; SNTP; Xmodem upgrade; cable diagnostics; ping; syslog; Telnet client (SSH secure support) Time-based port operation Link up or down based on user-defined schedule (when the port is administratively up) Login banner Configurable multiple banners for web as well as CLI |
| Power Efficiency | EEE Compliant (802.3az) Supports 802.3az on all copper ports Energy Detect Automatically turns power off on Gigabit Ethernet and 10/100 RJ-45 port when detecting link down Active mode is resumed without loss of any packets when the switch detects the link up Cable length detection Adjusts the signal strength based on the cable length for Gigabit Ethernet models. Reduces the power consumption for cables shorter than 10m. Disable port LEDs LEDs can be manually turned off to save on energy |
| General | Jumbo frames Frame sizes up to 9K (9216) bytes supported on 10/100 and Gigabit interfaces MAC table Up to 16K (16384) MAC addresses |
| Discovery | Bonjour The switch advertises itself using the Bonjour protocol Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) (802.1ab) with LLDP?MED extensions LLDP allows the switch to advertise its identification, configuration, and capabilities to neighboring devices that store the data in a MIB. LLDP-MED is an enhancement to LLDP that adds the extensions needed for IP phones Cisco Discovery Protocol The switch advertises itself using the Cisco Discovery Protocol. It also learns the connected device and its characteristics via Cisco Discovery Protocol |
| Power | Green Power (Mode) Energy detect short reach System Power Consumption 110 V=9.0 W 220 V=9.8 W Head Dissipation 16.4 BTU/hr |
| Ports | Total System Ports 10 x Gigabit Ethernet ports RJ-45 Ports 10 x Gigabit Ethernet ports Combo Ports (RJ-45+SFP) 2 SFP slots, 2 Gigabit Ethernet combo |
| Buttons | Reset buttons |
| Cabling Type | Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) Category 5 or better for 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX; UTP Category 5 Ethernet or better for 1000BASE-T |
| LEDs | System, Link/Act, PoE, Speed, LED power saving option |
| Flash | 256 MB |
| CPU Memory | 512 MB |
| Packet Buffer | 12 Mb |
| Power | 100-240 V, 50/60 Hz, 2.0 A, external |
| Certifications | UL (UL 60950), CSA (CSA 22.2), CE mark, FCC Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A |
| Temperature & Humidity | Operating Temperature: 32 to 104?F / 0 to 40?C Storage Temperature: -4 to 158?F / -20 to 70?C Operating Humidity: 10 to 90% relative, non-condensing Storage Humidity: 10 to 90% relative, non-condensing |
| Fan | Fanless design |
| MTBF | 367,209 hours @ 104?F / 40?C |
| Minimum Requirements | Web browser: Mozilla Firefox version 8 or later; Microsoft Internet Explorer version 7 or later, Safari, Chrome Category 5 Ethernet network cable TCP/IP, network adapter, and network operating system (such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, or Mac OS X) installed on each computer in the network |
| Dimensions | 280 x 44 x 170 mm (11.0 x 1.45 x 6.69 in) |
| Weight | 6.06 lb / 2.75 kg |
| Package Weight | 1.09 kg (2.40 lb) |
Warranty | 5 ปี |
ยังไม่มีการ review กรุณาเขียน review
ไม่มีคำถามที่ใช้ได้ ถามคำถามของคุณ

check_circle
check_circle